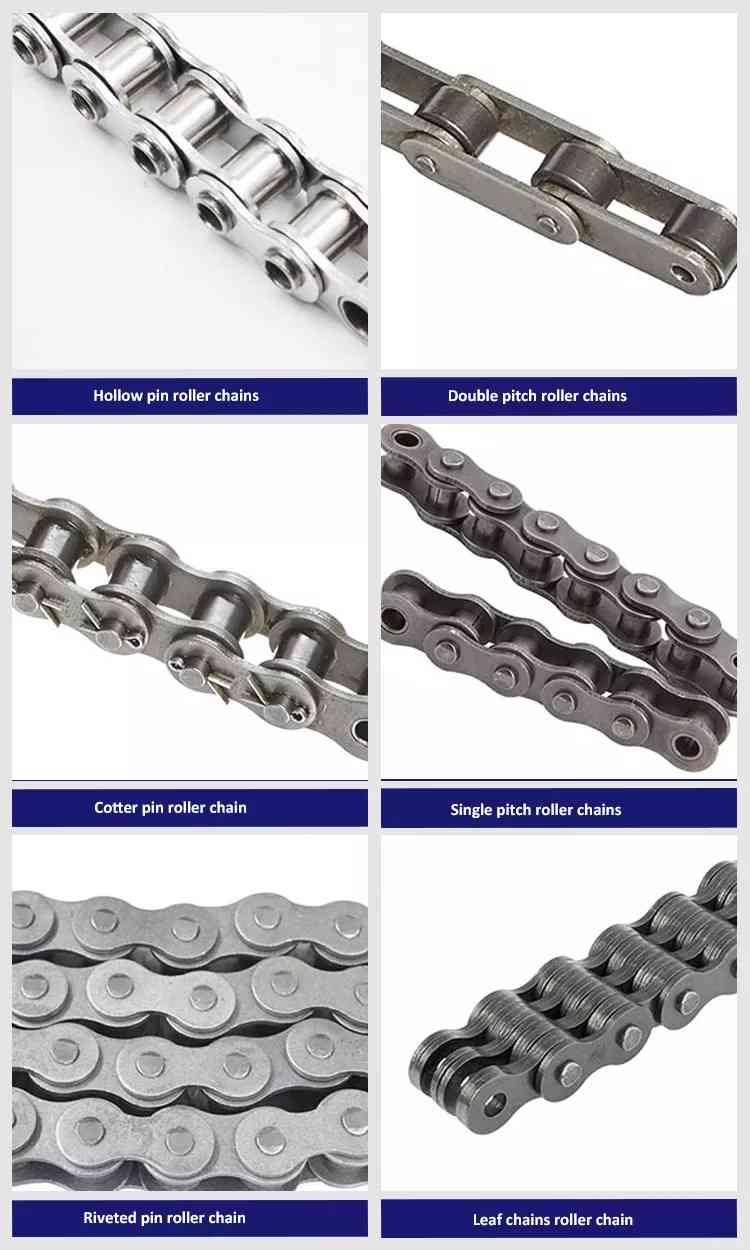
Product Description
A Series Short Pitch Precision Multiple Strand Roller Chains & Bush Chains
|
ANSI |
Chain No. |
Pitch
P |
Roller diameter
d1max |
Width between inner plates b1min mm |
Pin diameter
d2max |
Pin length | Inner plate depth h2max mm |
Plate thickness
Tmax |
Transverse pitch Pt mm |
Tensile strength
Qmin |
Average tensile strength
Q0 |
Weight per meter q kg/m |
|
| Lmax mm |
Lcmax mm |
||||||||||||
| 50-6 | 10A-6 | 15.875 | 10.16 | 9.40 | 5.08 | 111.3 | 112.8 | 15.09 | 2.03 | 18.11 | 133.2/29964 | 146.52 | 6.43 |
ROLLER CHAIN
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
CONSTRUCTION OF THE CHAIN
Two different sizes of roller chain, showing construction.
There are 2 types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having 2 inner plates held together by 2 sleeves or bushings CZPT which rotate 2 rollers. Inner links alternate with the second type, the outer links, consisting of 2 outer plates held together by pins passing through the bushings of the inner links. The “bushingless” roller chain is similar in operation though not in construction; instead of separate bushings or sleeves holding the inner plates together, the plate has a tube stamped into it protruding from the hole which serves the same purpose. This has the advantage of removing 1 step in assembly of the chain.
The roller chain design reduces friction compared to simpler designs, resulting in higher efficiency and less wear. The original power transmission chain varieties lacked rollers and bushings, with both the inner and outer plates held by pins which directly contacted the sprocket teeth; however this configuration exhibited extremely rapid wear of both the sprocket teeth, and the plates where they pivoted on the pins. This problem was partially solved by the development of bushed chains, with the pins holding the outer plates passing through bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This distributed the wear over a greater area; however the teeth of the sprockets still wore more rapidly than is desirable, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and provided rolling contact with the teeth of the sprockets resulting in excellent resistance to wear of both sprockets and chain as well. There is even very low friction, as long as the chain is sufficiently lubricated. Continuous, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of primary importance for efficient operation as well as correct tensioning.
LUBRICATION
Many driving chains (for example, in factory equipment, or driving a camshaft inside an internal combustion engine) operate in clean environments, and thus the wearing surfaces (that is, the pins and bushings) are safe from precipitation and airborne grit, many even in a sealed environment such as an oil bath. Some roller chains are designed to have o-rings built into the space between the outside link plate and the inside roller link plates. Chain manufacturers began to include this feature in 1971 after the application was invented by Joseph Montano while working for Whitney Chain of Hartford, Connecticut. O-rings were included as a way to improve lubrication to the links of power transmission chains, a service that is vitally important to extending their working life. These rubber fixtures form a barrier that holds factory applied lubricating grease inside the pin and bushing wear areas. Further, the rubber o-rings prevent dirt and other contaminants from entering inside the chain linkages, where such particles would otherwise cause significant wear.[citation needed]
There are also many chains that have to operate in dirty conditions, and for size or operational reasons cannot be sealed. Examples include chains on farm equipment, bicycles, and chain saws. These chains will necessarily have relatively high rates of wear, particularly when the operators are prepared to accept more friction, less efficiency, more noise and more frequent replacement as they neglect lubrication and adjustment.
Many oil-based lubricants attract dirt and other particles, eventually forming an CZPT paste that will compound wear on chains. This problem can be circumvented by use of a “dry” PTFE spray, which forms a solid film after application and repels both particles and moisture.
VARIANTS DESIGN
Layout of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Inner plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller
If the chain is not being used for a high wear application (for instance if it is just transmitting motion from a hand-operated lever to a control shaft on a machine, or a sliding door on an oven), then 1 of the simpler types of chain may still be used. Conversely, where extra strength but the smooth drive of a smaller pitch is required, the chain may be “siamesed”; instead of just 2 rows of plates on the outer sides of the chain, there may be 3 (“duplex”), 4 (“triplex”), or more rows of plates running parallel, with bushings and rollers between each adjacent pair, and the same number of rows of teeth running in parallel on the sprockets to match. Timing chains on automotive engines, for example, typically have multiple rows of plates called strands.
Roller chain is made in several sizes, the most common American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards being 40, 50, 60, and 80. The first digit(s) indicate the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the last digit being 0 for standard chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. Thus, a chain with half-inch pitch would be a #40 while a #160 sprocket would have teeth spaced 2 inches apart, etc. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch; thus a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but stainless steel is used in food processing machinery or other places where lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are occasionally seen for the same reason.
Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up using a master link (also known as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip rather than friction fit, allowing it to be inserted or removed with simple tools. Chain with a removable link or pin is also known as cottered chain, which allows the length of the chain to be adjusted. Half links (also known as offsets) are available and are used to increase the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the master link (also known as a connecting link) “riveted” or mashed on the ends. These pins are made to be durable and are not removable.
USE
An example of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain system
Roller chains are used in low- to mid-speed drives at around 600 to 800 feet per minute; however, at higher speeds, around 2,000 to 3,000 feet per minute, V-belts are normally used due to wear and noise issues.
A bicycle chain is a form of roller chain. Bicycle chains may have a master link, or may require a chain tool for removal and installation. A similar but larger and thus stronger chain is used on most motorcycles although it is sometimes replaced by either a toothed belt or a shaft drive, which offer lower noise level and fewer maintenance requirements.
The great majority of automobile engines use roller chains to drive the camshaft(s). Very high performance engines often use gear drive, and starting in the early 1960s toothed belts were used by some manufacturers.
Chains are also used in forklifts using hydraulic rams as a pulley to raise and lower the carriage; however, these chains are not considered roller chains, but are classified as lift or leaf chains.
Chainsaw cutting chains superficially resemble roller chains but are more closely related to leaf chains. They are driven by projecting drive links which also serve to locate the chain CZPT the bar.
Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 front (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain drive from an air motor
A perhaps unusual use of a pair of motorcycle chains is in the Harrier Jump Jet, where a chain drive from an air motor is used to rotate the movable engine nozzles, allowing them to be pointed downwards for hovering flight, or to the rear for normal CZPT flight, a system known as Thrust vectoring.
WEAR
The effect of wear on a roller chain is to increase the pitch (spacing of the links), causing the chain to grow longer. Note that this is due to wear at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from actual stretching of the metal (as does happen to some flexible steel components such as the hand-brake cable of a motor vehicle).
With modern chains it is unusual for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to wear until it breaks, since a worn chain leads to the rapid onset of wear on the teeth of the sprockets, with ultimate failure being the loss of all the teeth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in particular the smaller of the two) suffer a grinding motion that puts a characteristic hook shape into the driven face of the teeth. (This effect is made worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no matter what care is taken). The worn teeth (and chain) no longer provides smooth transmission of power and this may become evident from the noise, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing seen with a timing light. Both sprockets and chain should be replaced in these cases, since a new chain on worn sprockets will not last long. However, in less severe cases it may be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the smaller 1 that suffers the most wear. Only in very light-weight applications such as a bicycle, or in extreme cases of improper tension, will the chain normally jump off the sprockets.
The lengthening due to wear of a chain is calculated by the following formula:
M = the length of a number of links measured
S = the number of links measured
P = Pitch
In industry, it is usual to monitor the movement of the chain tensioner (whether manual or automatic) or the exact length of a drive chain (one rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center drive). A simpler method, particularly suitable for the cycle or motorcycle user, is to attempt to pull the chain away from the larger of the 2 sprockets, whilst ensuring the chain is taut. Any significant movement (e.g. making it possible to see through a gap) probably indicates a chain worn up to and beyond the limit. Sprocket damage will result if the problem is ignored. Sprocket wear cancels this effect, and may mask chain wear.
CHAIN STRENGTH
The most common measure of roller chain’s strength is tensile strength. Tensile strength represents how much load a chain can withstand under a one-time load before breaking. Just as important as tensile strength is a chain’s fatigue strength. The critical factors in a chain’s fatigue strength is the quality of steel used to manufacture the chain, the heat treatment of the chain components, the quality of the pitch hole fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other factors can include the thickness of the linkplates and the design (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous drive is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile strength, depending on the type of master links used (press-fit vs. slip-fit)[citation needed]. Roller chains operating on a continuous drive beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely via linkplate fatigue failure.
The standard minimum ultimate strength of the ANSI 29.1 steel chain is 12,500 x (pitch, in inches)2. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly decrease wear by means of internal lubricants, increasing chain life. The internal lubrication is inserted by means of a vacuum when riveting the chain together.
CHAIN STHangZhouRDS
Standards organizations (such as ANSI and ISO) maintain standards for design, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the following Table shows data from ANSI standard B29.1-2011 (Precision Power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][10] for additional information.
ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Ultimate Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
For mnemonic purposes, below is another presentation of key dimensions from the same standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking behind the choice of preferred numbers in the ANSI standard):
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
Notes:
1. The pitch is the distance between roller centers. The width is the distance between the link plates (i.e. slightly more than the roller width to allow for clearance).
2. The right-hand digit of the standard denotes 0 = normal chain, 1 = lightweight chain, 5 = rollerless bushing chain.
3. The left-hand digit denotes the number of eighths of an inch that make up the pitch.
4. An “H” following the standard number denotes heavyweight chain. A hyphenated number following the standard number denotes double-strand (2), triple-strand (3), and so on. Thus 60H-3 denotes number 60 heavyweight triple-strand chain.
A typical bicycle chain (for derailleur gears) uses narrow 1⁄2-inch-pitch chain. The width of the chain is variable, and does not affect the load capacity. The more sprockets at the rear wheel (historically 3-6, nowadays 7-12 sprockets), the narrower the chain. Chains are sold according to the number of speeds they are designed to work with, for example, “10 speed chain”. Hub gear or single speed bicycles use 1/2″ x 1/8″ chains, where 1/8″ refers to the maximum thickness of a sprocket that can be used with the chain.
Typically chains with parallel shaped links have an even number of links, with each narrow link followed by a broad one. Chains built up with a uniform type of link, narrow at 1 and broad at the other end, can be made with an odd number of links, which can be an advantage to adapt to a special chainwheel-distance; on the other side such a chain tends to be not so strong.
Roller chains made using ISO standard are sometimes called as isochains.
WHY CHOOSE US
1. Reliable Quality Assurance System
2. Cutting-Edge Computer-Controlled CNC Machines
3. Bespoke Solutions from Highly Experienced Specialists
4. Customization and OEM Available for Specific Application
5. Extensive Inventory of Spare Parts and Accessories
6. Well-Developed CZPT Marketing Network
7. Efficient After-Sale Service System
The 219 sets of advanced automatic production equipment provide guarantees for high product quality. The 167 engineers and technicians with senior professional titles can design and develop products to meet the exact demands of customers, and OEM customizations are also available with us. Our sound global service network can provide customers with timely after-sales technical services.
We are not just a manufacturer and supplier, but also an industry consultant. We work pro-actively with you to offer expert advice and product recommendations in order to end up with a most cost effective product available for your specific application. The clients we serve CZPT range from end users to distributors and OEMs. Our OEM replacements can be substituted wherever necessary and suitable for both repair and new assemblies.
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated|
|
|---|
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Food and Beverage Industry, Motorcycle Parts |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you ensure proper alignment of an industrial chain system?
Proper alignment of an industrial chain system is crucial for its efficient and reliable operation. Here are the steps to ensure proper alignment:
- Sprocket Alignment: Align the sprockets correctly along the same plane to ensure the chain runs smoothly. Check for any misalignment, such as lateral or angular misalignment, and adjust the sprockets accordingly.
- Tension Adjustment: Adjust the tension of the chain to the manufacturer’s specifications. An overly loose or tight chain can cause excessive wear and premature failure. Use appropriate tensioning devices or methods to achieve the recommended tension.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the chain as it operates. Observe its movement along the sprockets to ensure it tracks properly. Look for any signs of the chain riding on the sprocket teeth or deviating from its intended path.
- Measurement and Adjustment: Use alignment tools, such as a straightedge or laser alignment devices, to measure the alignment of the sprockets. Compare the measurements with the manufacturer’s specifications and make necessary adjustments to achieve proper alignment.
- Periodic Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the chain system to ensure continued alignment. Check for any wear or damage that may affect the alignment and address it promptly. Keep the chain properly lubricated to reduce friction and improve its movement along the sprockets.
- Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about the alignment or encounter persistent alignment issues, seek the assistance of a qualified professional or technician who has experience in industrial chain systems. They can provide expert guidance and ensure the proper alignment of the system.
By following these steps and maintaining proper alignment of the industrial chain system, you can minimize wear, reduce the risk of chain failure, and optimize the overall performance and longevity of the system.
How do you optimize the efficiency of an industrial chain system?
Optimizing the efficiency of an industrial chain system involves various factors and considerations. Here are some key steps to achieve maximum efficiency:
1. Proper Design: Ensure that the industrial chain system is designed correctly for the specific application. Consider factors such as load capacity, speed, environment, and required service life when selecting the chain and related components.
2. Adequate Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction, wear, and energy loss in the chain system. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricant type and quantity.
3. Correct Tensioning: Maintaining the right tension in the chain is crucial for optimal performance. Over-tensioning or under-tensioning can lead to increased wear, power loss, and premature failure. Regularly check and adjust the tension as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
4. Alignment and Sprocket Inspection: Ensure proper alignment of the chain and sprockets. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and energy loss. Regularly inspect the sprockets for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment, and replace or adjust as necessary.
5. Minimize Friction and Resistance: Reduce friction and resistance throughout the chain system by keeping the components clean and free from debris. Regularly clean and inspect the chain, sprockets, and guides to remove any accumulated dirt or contaminants.
6. Maintenance and Inspection: Implement a regular maintenance and inspection schedule for the entire chain system. This includes checking for wear, lubrication status, tension, and alignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and ensure optimal performance.
7. Training and Education: Provide proper training to operators and maintenance personnel on the correct handling, operation, and maintenance of the industrial chain system. This will help ensure that everyone understands the importance of efficiency and follows best practices.
By following these optimization strategies, the efficiency of an industrial chain system can be improved, leading to reduced energy consumption, extended service life, and cost savings in the long run.

Can an industrial chain be repaired or does it need to be replaced entirely?
Whether an industrial chain can be repaired or needs to be replaced entirely depends on the extent of damage and the type of chain. In some cases, minor issues with an industrial chain can be repaired, while in other cases, replacement may be necessary. Here are some considerations:
- Extent of damage: If the chain has minor issues such as a damaged link or a loose pin, it may be possible to repair it by replacing the damaged component. However, if the chain has significant damage, such as severe elongation or multiple broken links, it may be more cost-effective to replace the entire chain.
- Type of chain: The repairability of an industrial chain also depends on its construction and design. Some chains, such as roller chains, can be disassembled and repaired by replacing individual components. However, other types of chains, such as welded steel chains, may be difficult or impractical to repair and may require complete replacement.
- Manufacturer’s recommendations: It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations regarding repairs. The manufacturer can provide specific information on whether the chain can be repaired and the proper procedures to follow.
- Cost and time considerations: Repairing an industrial chain may require specialized tools, replacement parts, and technical expertise. It is important to consider the cost of repairs, including labor and materials, compared to the cost of a new chain. Additionally, repair time should be taken into account, as it may result in downtime for the equipment or production line.
Ultimately, the decision to repair or replace an industrial chain should be based on factors such as the extent of damage, the chain’s design, manufacturer’s recommendations, and cost-effectiveness. It is recommended to consult with a qualified technician or contact the manufacturer for guidance in making this determination.


editor by CX 2023-07-21